Glucagon: The Lifesaving Hormone You Need to Know
Introduction
Have you ever felt dizzy, lightheaded, or suddenly exhausted? These symptoms could be signs of low blood sugar levels, a condition your body counteracts with an essential hormone called glucagon. This unsung hero works behind the scenes to maintain blood sugar balance and prevent dangerous drops.
Let’s dive into what glucagon is, how it works, its benefits, and why it is vital for your overall health!
What is Glucagon?
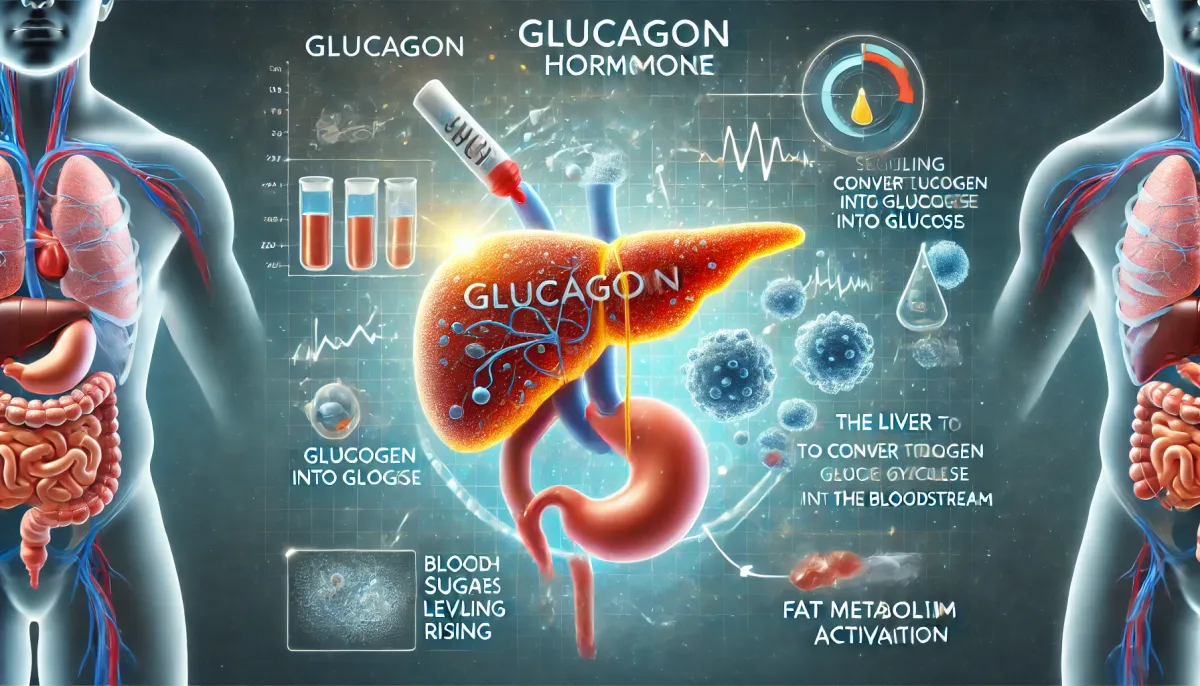
Glucagon is a hormone produced by alpha cells in the pancreas. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by acting in opposition to insulin. While insulin lowers blood sugar, glucagon raises it when it drops too low.
How Glucagon Works
When blood sugar levels fall below normal, the body triggers the release of glucagon, initiating the following processes:
- Stimulating the liver to release stored sugar – Glucagon signals the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream. This process is known as glycogenolysis.
- Producing new glucose from alternative sources – If glycogen stores are insufficient, the liver generates glucose from amino acids and fats through a process called gluconeogenesis.
- Balancing the body's energy supply – Glucagon promotes fat breakdown to provide additional energy when food intake is low or energy demands are high.
Benefits of Glucagon
Beyond regulating blood sugar, glucagon offers additional health benefits, including:
- Preventing hypoglycemia – Especially important for individuals with diabetes who take insulin.
- Enhancing fat metabolism – Some studies suggest glucagon may help with weight management by promoting fat breakdown.
- Medical applications – Injectable glucagon is used to treat severe hypoglycemia in diabetic patients.
Glucagon vs. Insulin: A Delicate Balance
Maintaining a balance between glucagon and insulin is essential for overall health. An imbalance can lead to conditions such as:
- Diabetes – Caused by insulin dysfunction, leading to abnormally high blood sugar levels.
- Chronic hypoglycemia – If glucagon function is impaired, recurrent low blood sugar episodes can occur.
Foods That Stimulate Glucagon Release
To promote glucagon release, the body must experience periods of low blood sugar or consume foods that encourage fat metabolism, such as:
- High-protein foods – Eggs, fish, lean meats, and legumes help shift the body into fat-burning mode.
- High-fiber foods – Leafy greens, beans, and whole grains help stabilize blood sugar and support glucagon function.
- Healthy fats – Olive oil, avocados, and nuts lower insulin levels and promote fat utilization.
- Intermittent fasting – Skipping meals intermittently can enhance glucagon secretion and promote fat-burning.
- Reducing processed carbohydrates – Limiting sugar and refined starches prevents insulin spikes and supports glucagon function.
Cardio Exercise and Glucagon: Should You Work Out on an Empty Stomach?
Cardio exercises such as running, swimming, and cycling can stimulate glucagon production, especially when performed in a fasted state.
Is It Beneficial to Do Cardio While Hungry?
Exercising when blood sugar is low (such as before breakfast or during intermittent fasting) may enhance glucagon activity, promoting fat and protein breakdown for energy. However, intense workouts on an empty stomach may lead to dizziness or fatigue.
For best results, opt for moderate-intensity cardio and listen to your body's signals. If you feel weak or lightheaded, consuming a small meal before exercise may be necessary.
How to Optimize Glucagon Function
- Eat balanced meals – Avoid prolonged fasting to prevent excessive reliance on glucagon.
- Exercise regularly – Physical activity helps balance hormone levels, including glucagon and insulin.
- Manage stress – Chronic stress affects hormonal balance and blood sugar regulation.
- Stay hydrated – Proper hydration supports metabolic processes and hormone function.
Conclusion
Glucagon is a key hormone that maintains stable blood sugar levels and prevents hypoglycemia. Working alongside insulin, it ensures a balanced energy supply for the body. By following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, you can optimize glucagon function for better overall health.
Have you ever experienced low blood sugar symptoms? Share your experience in the comments below!



